First certified simple-mount cluster ever!

End of January 2019 we have achieved a new milestone for our SLES for SAP Applications cluster solutions. We passed the SAP certification named “SAP S/4-HA-CLU 1.0” as the first cluster vendor. Now, end of November 2021, we are again the first vendor with a certification using the simple-mount cluster architecture.
We have selected SLES for SAP Applications 15 as platform for the certification. The difference between the certification for SAP S/4 HANA and the certification for SAP NetWeaver is that beginning with version ABAP platform 1809 SAP has changed to the new Enqueue Standalone Architecture (ENSA2).
You can find SUSE in the SAP Certified Solutions Directory.
What is the difference between simple-mount and classical cluster architecture?
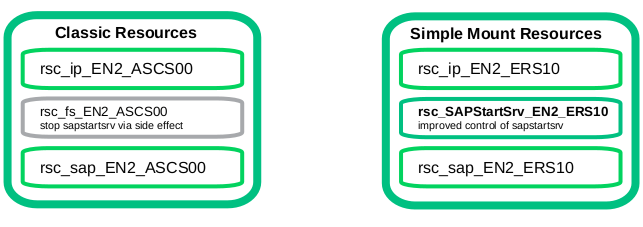
Customers told us that the classical filesystem structure for a cluster controlling the central services of the SAP application platform tends to be complex and error prone. As SUSE is keen to improve the customer experience we decided to simplify the cluster setup and filesystem structure. The result is the simple-mount structure for the SAP application platform. Instead of a number of filesystems needed per SAP system plus a number of filesystems per SAP instance the setup only needs a minimum. And the filesystems do not need to be switched-over and to be controlled by the pacemaker cluster. Typically systemd mounts these filesystems already during the system startup at boot time. The cluster controls the start and stop of the SAP start framework of each SAP instance and controls and monitors all integrated SAP instances as well.
Instead of the filesystem resources needed for each SAP instance we have added a new resource type SAPStartSrv controlling the matching sapstartsrv framework process. The cluster configuration is really straight forward.
As we see the simple-mount cluster architecture has so many benefits that is a good idea to use it for all new installations of ENSA1 and ENSA2 clusters on SLES for SAP Applications 15. The old cluster architecture is of course still supported.
Previous blog about simple-mount architecture.
About SAP certification criteria
SAP has defined certification criteria and goals:
- The architecture must be available in a two node (n=2) and a multiple node (n>2) cluster setup.
- The solution must be able to interact with the ENSA2 ASCS and ERS instances including the enqueue server and the enqueue replication server.
- The cluster must be able to migrate the ASCS to an optimal cluster node. For n>2 cluster nodes this should never be the ERS node, because then the replication would not be stretched over different nodes. The admin could trigger the migration by using the sapcontrol function HAFailoverToNode.
- The integration should provide an interface to set the maintenance mode of single instances using the sapcontrol command HASetMaintenanceMode and HACheckMaintenanceMode.
What is the difference between ENSA1 and ENSA2?
We already explained that beginning from ABAP platform 1809 SAP has changed from the former enqueue server (ENSA1) to ENSA2 by default. But what is the difference and how does that change affect the cluster?
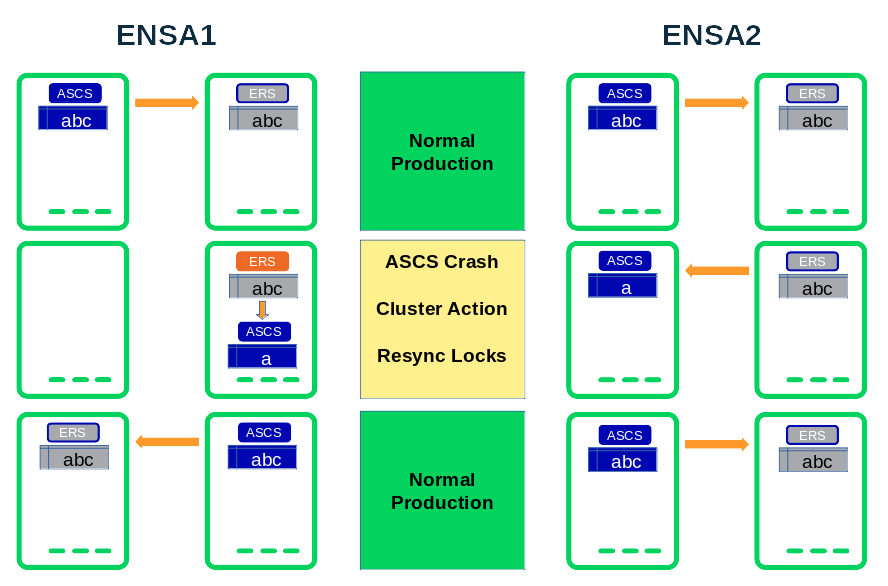
First of all let us have a look at the difference in the enqueue recovery after an ASCS failure (node or software):
ENSA1 vs. ENSA2 Lock Recovery
The enqueue recovery process in ENSA1 works on shared memory segments. This implies that the cluster needs to migrate the ASCS instance exactly to the node which has the synchronized lock table. So in ENSA1 the lock table recovery works by “mounting” the shared memory of the ERS (replicator) SAP instance. This handling has some disadvantages: The SAP system could lose the locks, if the ASCS does not start on the correct host. Also the replication is not stretched over multiple nodes for at least a short time period. And the setup is not perfect for clusters with more than 2 nodes.
The enqueue recovery process in ENSA2 works over the network. Once the ASCS (instance or node) fails, the cluster could restart it either on the same or any other cluster node. The ASCS instance processes the lock recovery by fetching the locks from the ERS over a network connection. For clusters with more than two nodes (n>2) this gives an optimal high availability scenario. The cluster could select any node where the ERS is currently not running. After the lock recovery the replication is already running over different hosts.
How does a simple-mount cluster look like?
The described architecture now includes the simple-mount structure based on an external network file share. Instead of the filesystem resources needed for each SAP instance a resource type SAPStartSrv controls the matching sapstartsrv framework process. The cluster configuration is straight forward. For SAP S/4HANA the concept implies that, after a resource failure, the ASCS does not need to be started at the ERS side.

Cluster Resources and Constraints
We recommend to follow our brand new setup guide “SAP S/4 HANA – Enqueue Replication 2 High Availability Cluster With Simple Mount – Setup Guide” available on our documentation web site Best Practices for SLES for SAP Applications 15. You will get the above new features and your cluster will be compatible with the certification goals.
Previous blog about simple-mount architecture.
This is Fabian Herschel and Lars Pinne blogging live from the SAP LinuxLab St. Leon-Rot, Germany. Please also read our other blogs about #TowardsZeroDowntime.
Related Articles
Apr 03rd, 2023
SUSE Linux Enterprise and SBOM support
Apr 15th, 2024
Install your HPC Cluster with Warewulf
Apr 26th, 2023